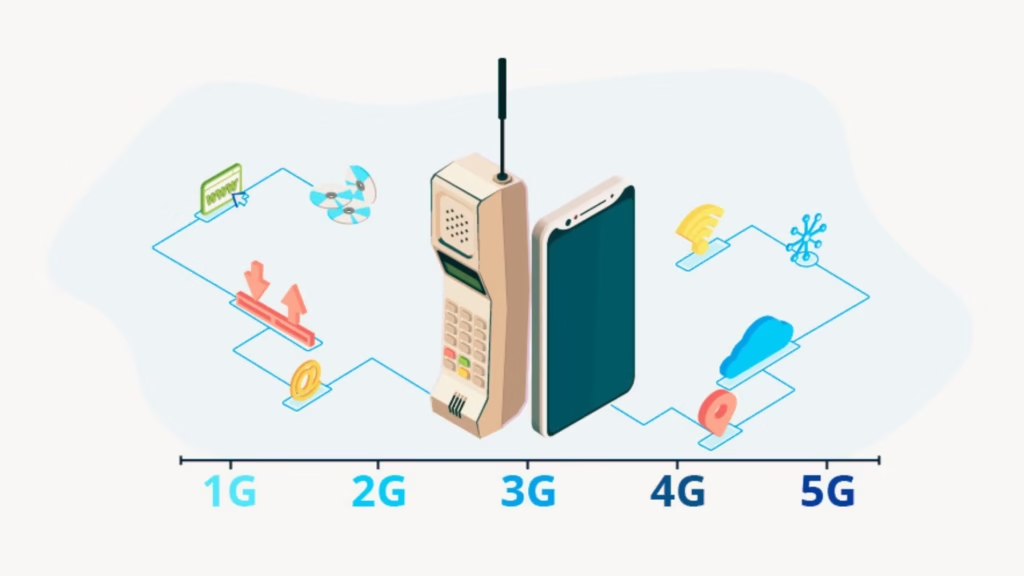
Mobile networks are the backbone of modern communication. From simple phone calls to streaming videos, mobile networks allow devices to connect wirelessly. Over the years, mobile technology has evolved from 2G to 5G, providing faster speeds, better coverage, and advanced features.
Understanding how mobile networks work helps people grasp the technology behind everyday communication.
What Are Mobile Networks?
A mobile network is a system that allows phones and other devices to communicate without wires. It uses radio waves and network towers to send and receive information. The network connects mobile devices to each other and to the internet.
Each generation of mobile networks—2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G—brings improvements in speed, connectivity, and capabilities.
2G Networks
2G, or second-generation networks, were introduced in the 1990s.
Key Features of 2G:
- Digital Signals: Replaced older analog networks
- Voice Calls: High-quality, reliable phone calls
- Text Messaging (SMS): First generation to support texting
- Basic Data Services: Limited internet browsing
2G networks laid the foundation for mobile communication and made phones more useful than just for voice calls.
3G Networks
3G networks appeared in the early 2000s, enabling faster data transmission.
Key Features of 3G:
- Mobile Internet: Allowed web browsing and emails on phones
- Video Calls: Made real-time video communication possible
- Apps and Media: Enabled apps for messaging, music, and navigation
- Better Coverage: Improved connectivity in urban and rural areas
3G networks marked the beginning of smartphones and mobile apps.
4G Networks
4G, or fourth-generation networks, brought high-speed internet to mobile devices.
Key Features of 4G:
- Fast Internet: Supports video streaming, online gaming, and HD calls
- Mobile Apps: Enhanced app performance with faster data
- VoLTE: Voice over LTE allows high-quality phone calls
- Improved Latency: Reduces delays in communication
4G networks transformed mobile devices into powerful tools for entertainment, work, and social connection.
5G Networks
5G is the latest generation, offering ultra-fast internet and low latency.
Key Features of 5G:
- High Speed: Download movies in seconds, stream in 4K/8K
- Low Latency: Near-instant response for gaming, AR, and VR
- IoT Connectivity: Supports smart homes, cities, and devices
- Network Slicing: Allocates bandwidth for different needs efficiently
5G is not just for phones—it enables connected devices, autonomous vehicles, and advanced healthcare applications.
How Mobile Networks Work Step by Step
- Your Device Sends a Signal: When you make a call or use the internet, your phone sends a radio signal to the nearest tower.
- Tower Connects to Network: The tower forwards the signal to the mobile network, which may involve multiple towers or base stations.
- Routing the Signal: The network directs the signal to its destination—another phone, a website, or a server.
- Data Transfer: Information moves through cell towers, fiber cables, and routers to reach the recipient quickly.
- Receiving Device: The recipient’s device receives the signal and translates it back into sound, images, or text.
This process happens in milliseconds, making real-time communication possible.
Differences Between Generations
| Feature | 2G | 3G | 4G | 5G |
| Speed | Low | Medium | High | Ultra-high |
| Voice Calls | Yes | Yes | VoLTE | VoNR (Voice over New Radio) |
| Internet Browsing | Limited | Basic | Fast | Lightning-fast |
| Video Streaming | No | Low-quality | HD | 4K/8K |
| Latency | High | Medium | Low | Very Low |
| IoT Support | No | Limited | Moderate | Extensive |
Benefits of Mobile Networks
- Global Connectivity: Stay connected anywhere, anytime
- Access to Information: Internet, news, and apps at your fingertips
- Business and Education: Work, learning, and collaboration online
- Entertainment: Streaming, gaming, and social media
- Innovation: Enables smart devices and future technologies
Mobile networks make modern life faster, easier, and more connected.
Challenges of Mobile Networks
- Coverage Gaps: Rural or remote areas may have limited access
- Security Risks: Data can be intercepted without proper protection
- High Costs: Infrastructure for 5G and maintenance can be expensive
- Device Compatibility: Older devices may not support new generations
Despite challenges, ongoing innovation improves access, speed, and reliability.
Final Thoughts
Mobile networks from 2G to 5G have transformed communication and society. They enable voice calls, text messages, video calls, streaming, gaming, smart devices, and even autonomous technology. Understanding how mobile networks work helps users appreciate the technology behind everyday life.
Platforms like 3basequinte demonstrate how structured and interactive platforms rely on reliable communication networks to provide real-time engagement and strategic decision-making tools.
By learning about mobile networks, we can understand how technology connects people, enhances productivity, and shapes the modern digital world.

